German Stem Cell Engineering:
The Science of a Better You
Stem cells are your body’s basic building blocks. They possess limitless therapeutic potential for many diseases, one of which is the aging process itself. The main focus of stem cell research has been the investigation of the potential of stem cells for its medical application, while established medicine has not even considered stem cells as a novel treatment option for many diseases. They have not worked harmoniously together yet.
ANOVA Institute for Regenerative Medicine bridges this gap, as it was founded with the main focus to achieve excellence in translational medicine. We are a German medical institute that offers individualized treatments for patients. We employ licensed and state-of-the-art stem cell-based methods while operating with the highest possible safety and quality standards.
Stem Cell Therapies sorted by stem cell type (source tissue) and product
How Does the ANOVA Therapy Differ?
Diagnostics – We Look for the Cause of Your Pain
Dr. mult. Michael K. Stehling, the founder of ANOVA IRM and the Vitus Prostate Center , is a radiologist (MD) and holds a PhD in physics. For this reason, the ANOVA Institute for Regenerative Medicine, in cooperation with the Prof. Stehling Institute for Diagnostic Imaging located in the same building, has the capability to use special precision diagnostics such as arthro-MRI and non-radioactive contrast MRIs.
Compared to many conventional MRIs, these methods are often able to localize the pain-causing inflammation in your joints. This enables us to determine individually how patients should be treated and where the stem cells should be applied.
Furthermore, in consultation with you, we supplement our patient-specific diagnostics with specific blood tests on hormones, inflammation parameters and other factors that are important in your case, or recommend further examinations such as a preventive MRI spinal scan.
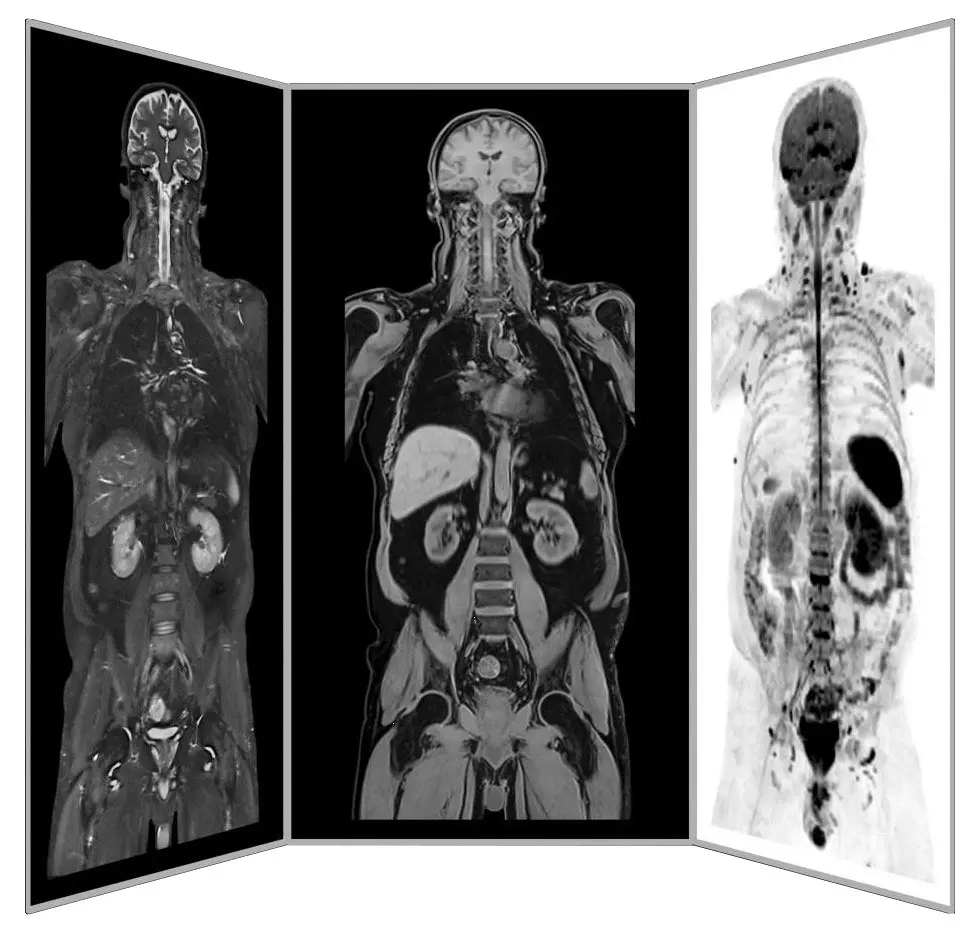
Precision MRI scans - find the source of pain
ANOVA IRM © Siemens Healthcare GmbH
Contraindications
Our stem cell treatments are experimental, but we only treat patients for whom we believe the risk/benefit ratio indicates treatment based on the state of the art, i.e., medical, scientific evidence.
Please understand that we therefore do not treat patients for whom the following points apply:
- Active cancer in the last two years
- Not yet of legal age
- Existing pregnancy or lactation period
- Unable to breathe on own, ventilator
- Difficulty breathing in supine position
- Dysphagia (extreme difficulty swallowing)
- Psychiatric disorder
- Active infectious disease (Hepatitis A, B, C, HIV, Syphilis, or other)
How Does the ANOVA Therapy Differ?
We Implant the Stem Cells Precisely Where They are Needed
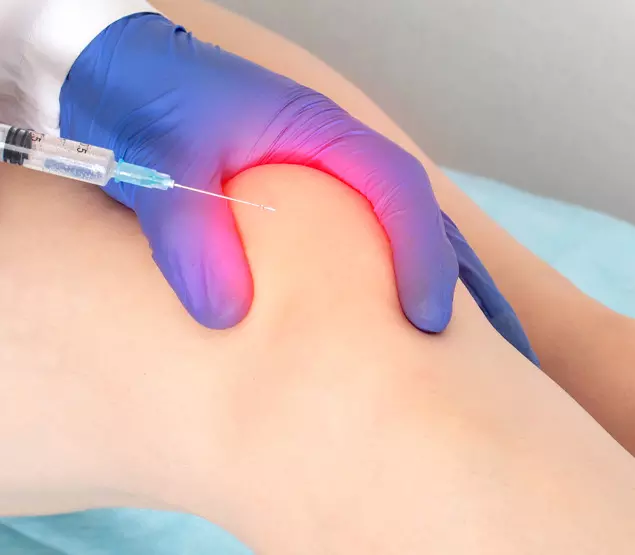
Stem cell injection into joints
ANOVA IRM Germany
Based on our specific diagnostics using arthro-MRI and non-radioactive contrast medium MRIs, we can, in contrast to many other clinics, deliver the stem cells with image support, e.g. using CT, precisely to the affected area. This means we can inject into and at joints to specifically and quickly trigger an effect where inflammation causes pain. All interventions are perfomed under supervision and care of our anesthesiologist and are pain free.
A purely intravenous administration, as many other clinics do, is only performed for the secretome (exosomes) if this is to be used additionally as a supportive or preventive measure because joint problems are present in several places in the body as the secretome is aimed to centrally modulate the immune response in order to inhibit over-reactions.
Of course, we will thoroughly advise you in the early process and the on-site consultation in advance on all steps and discuss alternatives and expectations.
Are you Interested but Unsure?
Book a Counseling Appointment!
Our patient care managers are happy to inform you about what information we need upfront (MRI, CT, X-ray), how to transfer large data files and schedule a counseling appointment with our physicians for you. Please use our contact form to support a fast processing of your case and request.
You are also always welcome to send us an e-mail about your case. The counseling appointment may also take place per telephone or video chat if you live outside Germany. For more intense counseling or additional diagnostic evaluations you may also book an on-site appointment. We can perform needed MRI on the same day. All services rendered by our patient care team are free of charge and we inform you about all physician appointment charges up-front.
Avoid joint replacement with stem cell treatment
ANOVA IRM - Germany
German Stem Cell Engineering – Designed for your Needs
ANOVA is proud to introduce the latest Stem Cell 2.0 Therapy - The Stem Cell Secretome Therapy. As the first clinic in Europe to have obtained the license to employ this treatment, we have developed a method that uses stem cells as a “factory” to mass produce the paracrine factors (= the essence of the stem cell regenerative potential) in high concentrations. Our method is designed and optimized to ensure high product quality and patient safety.
Our regenerative medicine programs are suitable for a variety of diseases and conditions. Whether you suffer from a sport injury which you want to heal quickly, or from a neurodegenerative disease - stem cell therapy may be a suitable option for you. With our holistic approach we ensure that the focus lies on your individual needs.
If you have any questions regarding our stem cell-based therapies please feel free to give us a call or simply contact us by e-mail. ANOVA's specialists are looking forward to answering your questions on stem cells in detail. All cases are carefully evaluated on an individual basis with our highly competent Doctors and Scientists.
Schedule an appointment today: +49 (69) 50 50 00 944